Everyone knows that you need the latest and greatest game consoles or graphics cards to get the best graphics, but what about the overall image quality? Buying a monitor is what is going to determine your overall viewing experience more than anything else – it doesn't matter if you have an RTX 3000 series-powered PC if you're stuck on a 2000s sub-HD monitor. /P> ContentsThe Basics:Common Video Ports and Their UsePanel Type:TN, IPS, or VA?Resolution and Size or Pixels Per Inch (PPI)Refresh Rate, Response Time, and Adaptive SyncLittle Things Matter TooWords of Parting
So let's get to it:how do you choose the best monitor for your needs?
Before you buy a monitor, you need to make sure it has a video port that's compatible with your current hardware. If not, you will need an adapter. Here are the common video ports you'll see when buying modern monitors, in order of prevalence:

TN panels excel at high refresh rates and fast response times at a lower price point than the competition, making them ideal for gamers and budget users. However, they also suffer from poor viewing angles and color reproduction, making them poor for professional work or multimedia viewing.
IPS panels excellent in viewing angles and color reproduction, but at a higher price than the competition. Cheap IPS panels can also have limited refresh rates and response times, but high-end IPS panels excel there for a higher price than TN. Most IPS panels also suffer from some degree of backlighting, which makes them slightly worse overall when viewing darker scenes in games or in the cinema.
VA panels excellent at viewing dark scenes and generally have good color reproduction and viewing angles at a balanced price. However, overall viewing angles and color reproduction don't match IPS, and response time is generally particularly poor on VA panels, making them less ideal for competitively-focused gamers. P>
If you were to compare identical but different resolution screens side by side, the one with the higher resolution will look sharper and clearer. This is because there is a higher PPI (pixels per inch) on the higher resolution screen, which helps display more detail.
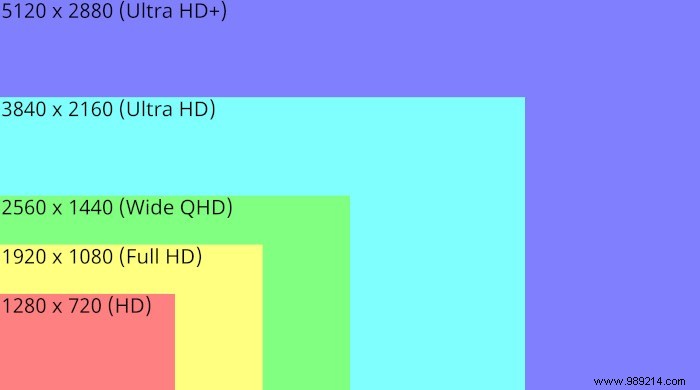
For PC monitors at a regular viewing distance, 1080p (1920×1080) looks pretty good at 24 inches and below, as it hits and exceeds 90 PPI, which is the baseline where monitors are sharp. Here are some other PPI/resolution sizes and targets, for your reference:
Adaptive Sync (called G-Sync by Nvidia or FreeSync by AMD), is a monitor technology used to synchronize the refresh rate of the monitor with the frame rate of the game without the need for something like V-Sync or RivaTuner Scanline Sync. This eliminates screen tearing without introducing additional latency, making it a must-have feature for gamers.
Refresh rate refers to the number of screen refreshes per second. 60Hz is the base refresh rate, but pushing to 144Hz and above will result in significantly improved gaming performance.
Response time is a somewhat related spec that if kept low (better) will reduce ghosting and smearing. TN panels have the best response time.
Also pay close attention to things like adjustable monitor stands, VESA wall mounts, and even built-in webcams and microphones. Features like these don't usually add as much to the price, but can make a big difference in the user experience for those looking for it.

By following the guide above, you should now know what to look out for when buying a monitor. You can also learn what to look for when buying a motherboard or processor.
Image credit:Evolved Wiki at WikiMedia Commons For video ports image; LG on Flickr For monitor panel image; PantheraLeo1359531 at WikiMedia Commons For resolution image editing