While it used to be a relatively specialized branch of mathematics and computer science, new predictive technologies are more accessible and easily applicable:companies use it on customers, researchers use it on diseases , ad agencies use it to target consumers, banks use it to prevent fraud , and the list goes on. So how does predictive analytics really work, what does it predict, and how reliable are its predictions?
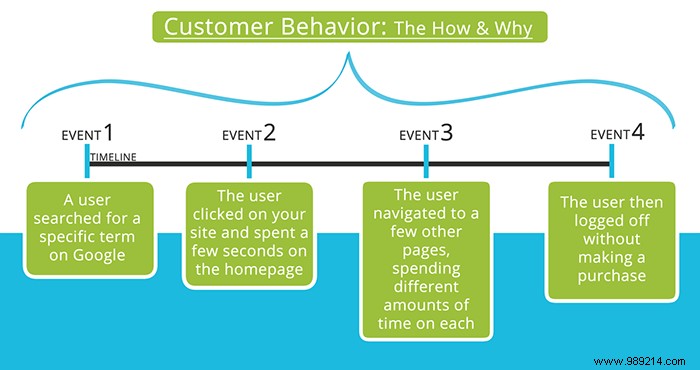
Predictive analytics is used productively in medical research, finance, manufacturing, supply chains and elsewhere, but one of the most profitable applications of this technology is to analyze and predict the behavior of clients. If you've ever wondered why your data is such a valuable commodity, this is one of the main reasons. With access to large amounts of historical user data, it is much easier for businesses to understand how they may be pushing consumer buttons.
In healthcare and medicine, predictive analytics is primarily used to optimize treatments and find new ways to fight disease. By analyzing historical patient data, hospitals can reduce the number of patients who need to return, create more personalized treatment plans, and get more accurate risk assessments. Predictive analytics models are also important for disease research, using patient and population-generated data to identify risk factors, treatment outcomes, and more.
Finance applications are also risk-driven – specifically, who is a safe bet for a loan or an account? Applying predictive analytics can help financial institutions identify those at high risk of default and more effectively flag fraudulent activity.
But no industry is as excited about predictive analytics as retail and advertising. Imagine if you could monitor your customer's every move, feed it into a massive database, and analyze it to look for patterns. You can find out who is most likely to stop using your service, what drives people to continue using your product, who is most likely to respond to certain ads, who to target with your campaigns, all with data that can be updated and analyzed in real time. time.
There is no single answer to this question, as each model is different. The quality of the data, the methods used to analyze it, and a host of other factors all play into the accuracy of the forecasts. Predictive analytics doesn't get it right all the time, but thanks to advances in big data and artificial intelligence, it's getting it right Continued time.
What makes big data "big" is not necessarily its quantity, but the efficiency with which large amounts can be processed. Much of the statistics have historically been based on guesses about populations based on samples drawn from those populations, which adds a layer of uncertainty.
Big data tools, however, allow much more available data to be used to make predictions, making them much more likely to be correct. Predictive analytics already does a pretty good job showing people announcements and determining travel times, and it's only going to get better in the future.
How to make the right decisions? For most of human history, we have used our brains to process all available input and act on it. Our decisions have always been marred by a lack of accurate information, a limited ability to identify patterns and a number of biases.
A well-designed algorithm with a large data set, however, doesn't have this problem, and the ability to offload much of our mental work onto machines is a big step forward for humanity. Of course, algorithms can be intentionally or unintentionally biased, datasets can be corrupted, and behavior predictions can be used for social control as easily as they can be used to optimize retail experiences. Ensuring that our systems develop to be transparent and generally beneficial will have a real impact on how technology shapes (and predicts) the future.
Image credits:Visual representation of the events that make up the behavioral analysis, Predictive analysis process